產品中心
產品資料
產品名稱: pBAD/Thio-TOPO
產品型號:
產品展商: HZbscience
產品文檔: 無相關文檔
簡單介紹
pBAD/Thio-TOPO的各批次質粒菌株發貨前均經過嚴格的多重驗證,如存在質量問題,請在收到產品的三個月內通知我司。收到pBAD/Thio-TOPO后請短暫離心,取2μl轉化至對應感受態中,挑取單克隆重新提取質粒后使用。
pBAD/Thio-TOPO
的詳細介紹
pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體基本信息
| 載體名稱: | pBAD/Thio-TOPO |
|---|---|
| 質粒類型: | 大腸桿菌表達載體;誘導表達載體 |
| 高拷貝/低拷貝: | 低拷貝 |
| 克隆方法: | TOPO-TA |
| 啟動子: | araBAD |
| 載體大小: | 4454 bp |
| 5' 測序引物及序列: | Trx Forward: 5′-TTCCTCGACGCTAACCTG-3′ |
| 3' 測序引物及序列: | pBAD Reverse 5′-GATTTAATCTGTATCAGG-3′ |
| 載體標簽: | V5 Epitope(C-端), 6x His Tag(C-端); HP-Thioredoxin(N-端),EK 切割位點 |
| 載體抗性: | 氨芐青霉素(Ampicillin) |
| 克隆菌株: | TOP10 |
| 表達菌株: | 推薦LMG194 |
| 備注: |
pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體是阿拉伯糖調控載體 ,在無葡萄糖的培養基中,阿拉伯糖正向調控目 的基因的表達; 通過調節阿拉伯糖的濃度水平來優化目的蛋白的可溶性表達; 采用TOPO-TA技術,只用5分鐘即可將PCR片段連接 到載體上去; pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體表達硫氧還蛋白 (thioredoxin,Trx)融合蛋白,硫氧還蛋白可增加目的蛋白的可溶性,提高蛋白產量。 |
| 產品目錄號: | K370-01 |
| 穩定性: | 穩表達 |
| 組成型/誘導型: | 誘導型(阿拉伯糖) |
| 病毒/非病毒: | 非病毒 |
pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體質粒圖譜和多克隆位點信息
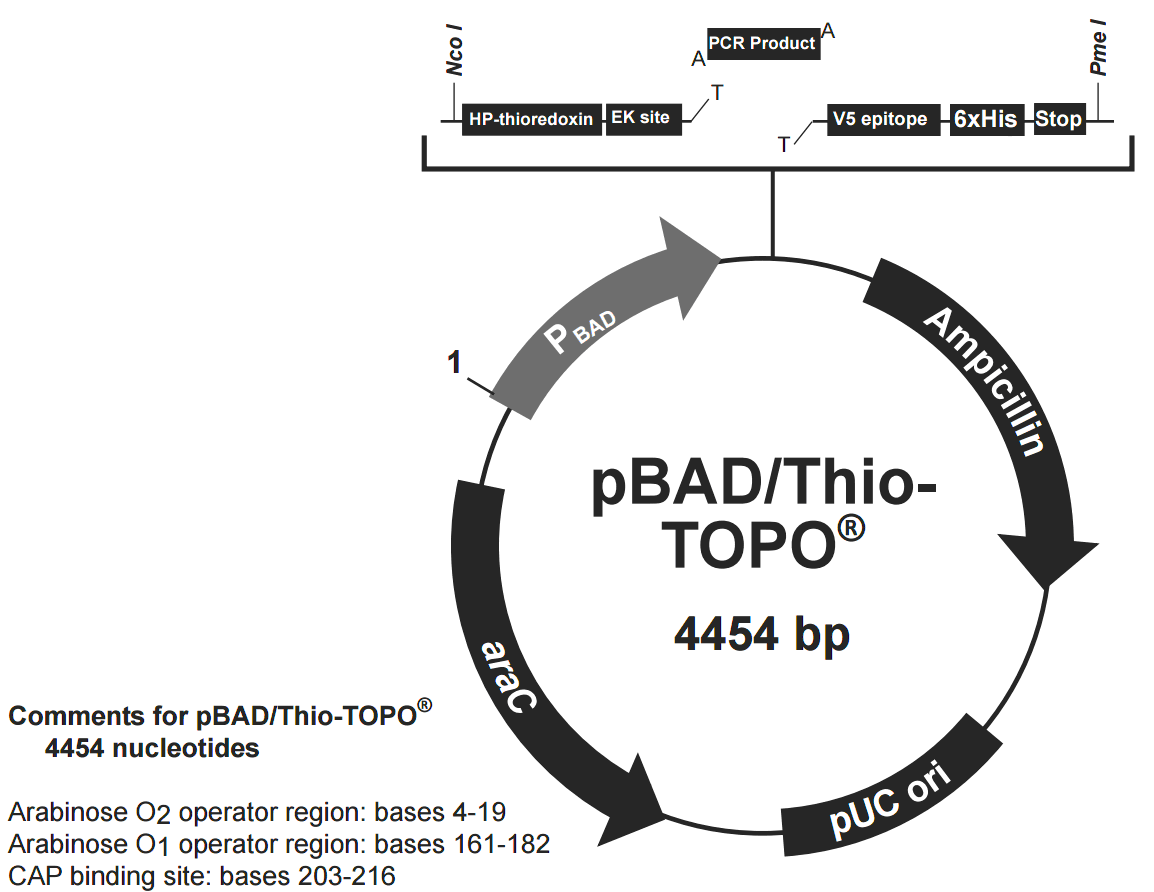

pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體簡介
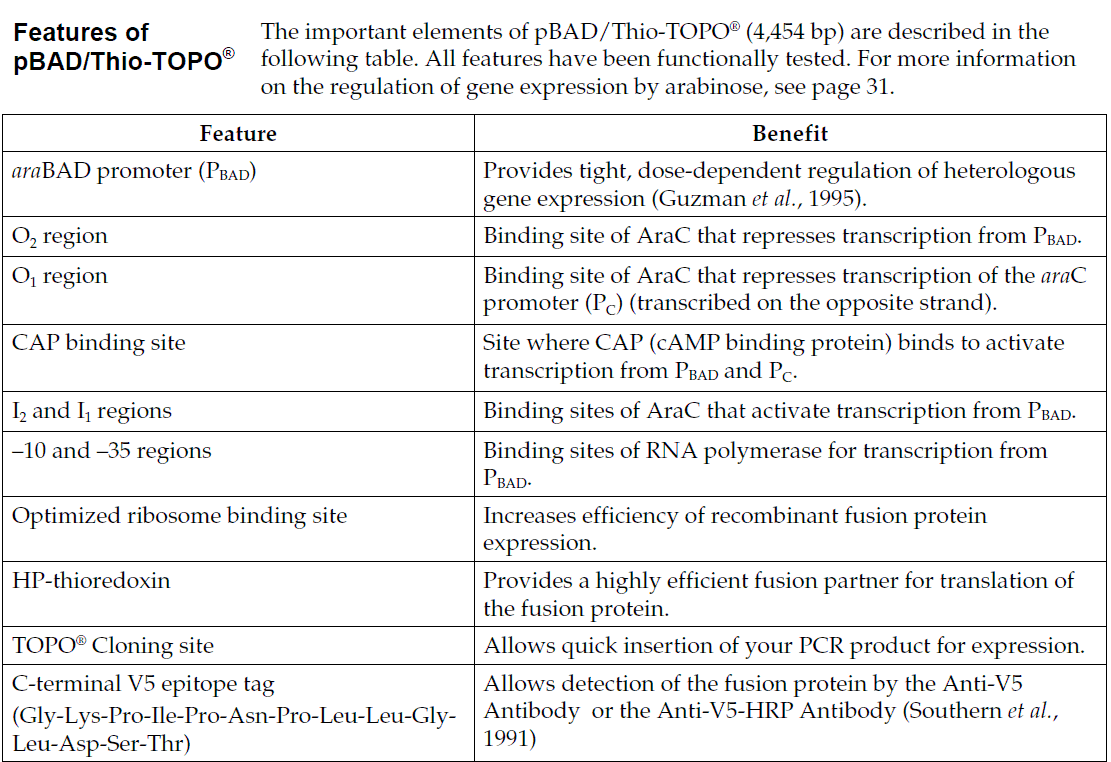
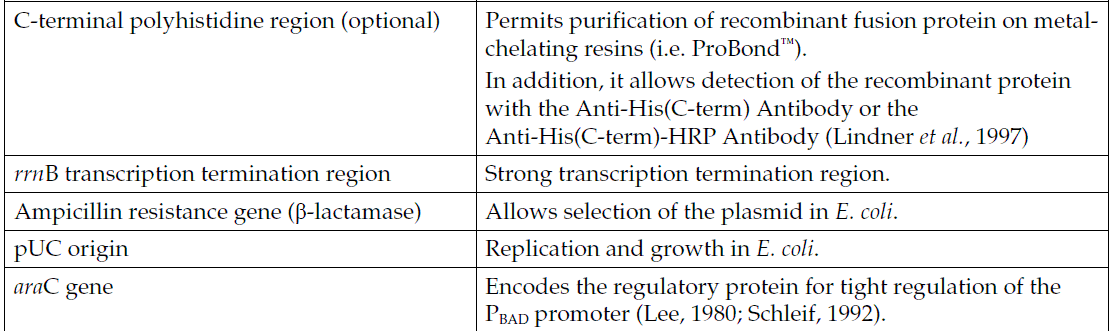
The pBAD/TOPO ThioFusion Expression Kit is designed for one-step cloning and regulated expression of thioredoxin fusion proteins in E. coli(Figure 1). The pBAD/Thio-TOPO vector encodes His-Patch thioredoxin as an N-terminal fusion partner. The thioredoxin fusion can significantly increase the solubility of many difficult-to-express proteins and improve the yield of protein production. pBAD/Thio-TOPO 載體具有以下特點:
The araBAD promoter for tightly regulated expression in E. coli I-activated vector for 5-minute TOPO Cloning of Taq-amplified PCR products
C-terminal polyhistidine (6xHis) tag for purification with nickel-chelating resin and detection with an Anti-His(C-term) Antibody
C-terminal V5 epitope for detection with an Anti-V5 Antibody
Enterokinase cleavage site for efficient cleavage of N-terminal fusion tag with EKMax Enterokinase
pBAD/TOPO ThioFusion Expression Kit provides a highly efficient, 5-minute, one-step cloning strategy ("TOPO Cloning") for the direct insertion of Taq polymerase-amplified PCR products into a plasmid vector for soluble, regulated expression and simplified protein purification in E. coli. No ligase, post-PCR procedures, or PCR primers containing specific sequences are required. Expression in E. coli is driven by the araBAD promoter (PBAD). The AraC gene product encoded on the pBAD/Thio-TOPO plasmid positively regulates this promoter. Recombinant proteins are expressed as fusions to His-Patch thioredoxin for high-level expression and simple purification. L-阿拉伯糖調控表達 In the presence of arabinose, expression from PBAD is induced while only very low levels of transcription are observed from PBAD in the absence of arabinose (Lee, 1980; Lee et al., 1987). Uninduced levels are repressed even further by growth in the presence of glucose (0.1% to 0.2%). Glucose reduces the levels of 3′, 5′-cyclic AMP, lowering expression from the catabolite-repressed PBAD promoter (Miyada et al., 1984). By varying the concentration of arabinose, protein expression levels can be optimized to ensure maximum expression of protein. In addition, the tight regulation of PBAD by AraC is useful for expression of potentially toxic or essential genes (Carson et al., 1991; Dalbey and Wickner, 1985; Guzman et al., 1992; Kuhn and Wickner, 1985; Russell et al., 1989; San Millan et al., 1989). 硫氧還蛋白 The 11.7 kDa thioredoxin protein is found in yeast, plants, and mammals, as well as in bacteria. It was originally isolated from E. coli as a hydrogen donor for ribonuclease reductase (for a review, see Holmgren, 1985 ). The gene has been completely sequenced (Wallace and Kushner, 1984). The protein has been crystallized and its three-dimensional structure determined (Katti et al., 1990).
When overexpressed in E. coli, thioredoxin is able to accumulate to approximately 40% of the total cellular protein and still remains soluble. Thioredoxin is used to increase translation efficiency, and in some cases, solubility, of eukaryotic proteins expressed in E. coli. Murine interleukin-2, human interleukin-3, murine interleukin-4, murine interleukin-5, human macrophage-colony stimulating factor, murine steel factor, murine leukemia inhibitory factor and human bone morphogenetic protein-2 are some of the proteins that have been produced as soluble C-terminal fusions to the thioredoxin protein in E. coli (LaVallie et al., 1993). 帶有組氨酸補丁的硫氧還蛋白 To create a metal binding domain in the thioredoxin protein, the glutamate residue at position 32 and the glutamine residue at position 64 were mutated to create histidine residues. When His-Patch thioredoxin folds, the histidines at positions 32 and 64 interact with a native histidine at position 8 to form a "patch". This histidine patch was shown to have high affinity for divalent cations (Lu et al., 1996). His-Patch thioredoxin (HP-thioredoxin) proteins can therefore be purified on metal-chelating resins (e.g., ProBond )
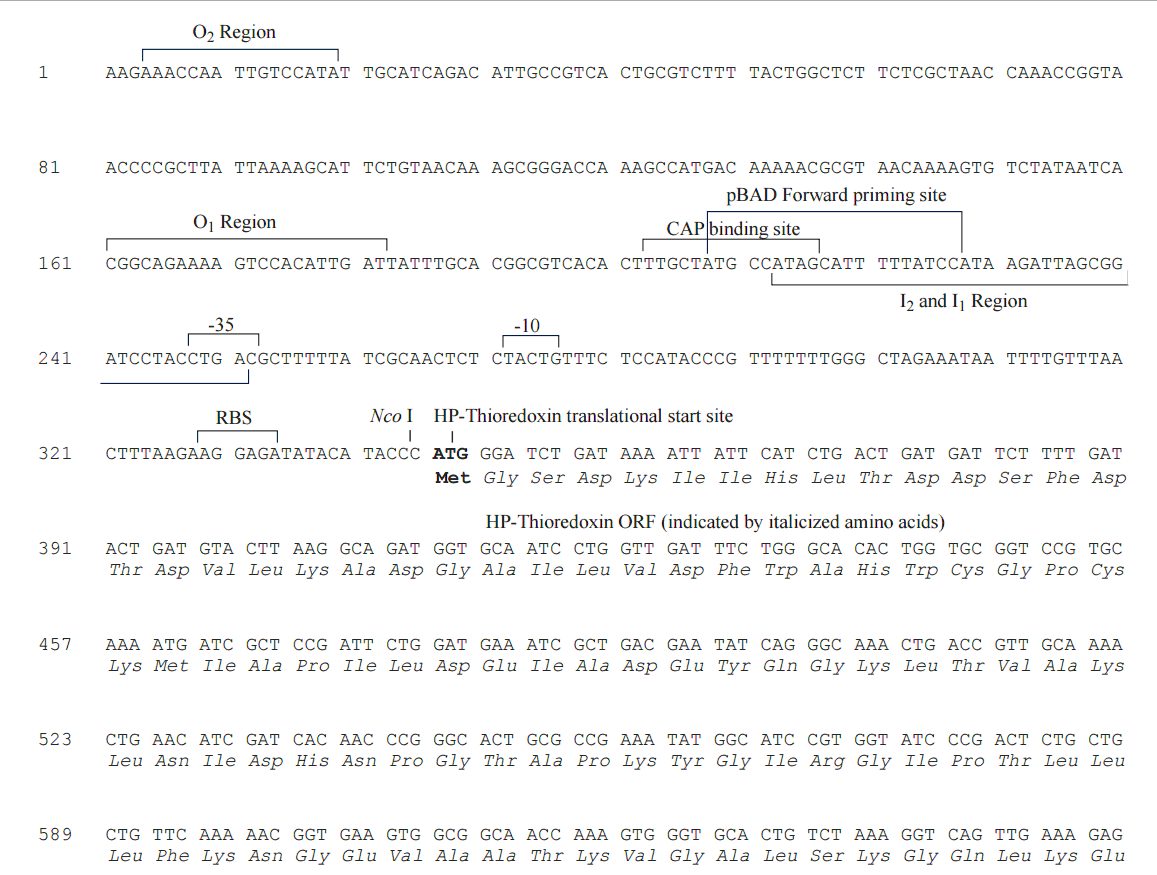
pBAD/Thio-TOPO載體序列
hz-2353R Mast Cell Chymase 肥大細胞類糜蛋白酶1抗體hz-0972R Gentamicin 慶大霉素抗體
hz-0973R Tetracycline 四環素抗體
hzm-0972M Gentamicin(3G7) 慶大霉素單克隆抗體
hz-0974R Oxytetracycline 土霉素抗體
hz-2059R Metronidazole 甲硝唑抗體
hzm-2059M Metronidazole(1C2) 甲硝唑單克隆抗體
hz-5741R MARK2 絲氨酸/蘇氨酸蛋白激酶MARK2抗體
hz-5742R phospho-MARK2(Thr595) 磷酸化絲氨酸/蘇氨酸蛋白激酶MARK2抗體
hz-3516R WBSCR14/ChREBP 糖類應答元件結合蛋白ChREBP抗體
hz-5743R CDKN3 細胞周期蛋白依賴性激酶抑制蛋白3抗體
hz-0236R ChRM2/Acetylcholine receptor(M2) 毒蕈堿型乙酰膽堿受體抗體
hz-1150R ChRM1/Acetylcholine receptor(M1) 毒蕈堿型乙酰膽堿受體M1抗體
hz-0441R ChRM2 毒蕈堿型乙酰膽堿受體M2抗體
hz-5744R CABLES2 細胞周期蛋白依賴性激酶CABLES2抗體
hz-1289R ChRM3/Acetylcholine receptor(M3) 毒蕈堿型乙酰膽堿受體M3抗體
hz-5745R CKS1 細胞周期蛋白依賴性激酶調節亞基1抗體
hz-0544R CIDEB 促進凋亡基因抗體
hz-1682R CIB1 鈣整合素結合蛋白1抗體
hz-0670R C-jun/AP-1 原癌基因蛋白/活化蛋白1抗體
關于我們
產品中心
服務中心
Copyright@ 2003-2025
上海滬震實業有限公司版權所有
電話:021-60345367
傳真:021-31320307
地址:上海市楊浦區密云路1018號復旦科技園808室
郵編:200612

