產品中心
產品資料
產品名稱: pBad/His A
產品型號:
產品展商: HZbscience
產品文檔: 無相關文檔
簡單介紹
pBad/His A的各批次質粒菌株發貨前均經過嚴格的多重驗證,如存在質量問題,請在收到產品的三個月內通知我司。收到pBad/His A后請短暫離心,取2μl轉化至對應感受態中,挑取單克隆重新提取質粒后使用。
pBad/His A
的詳細介紹
pBad/His A載體基本信息
| 載體名稱: | pBAD/His A |
|---|---|
| 質粒類型: | 大腸桿菌表達載體;誘導表達載體 |
| 高拷貝/低拷貝: | 低拷貝 |
| 克隆方法: | 限制性內切酶;多克隆位點 |
| 啟動子: | araBAD |
| 載體大小: | 4102 bp |
| 5' 測序引物及序列: | pBAD Forward: 5′-ATGCCATAGCATTTTTATCC-3′ |
| 3' 測序引物及序列: | pBAD Reverse 5′-GATTTAATCTGTATCAGG-3′ |
| 載體標簽: | 6x His Tag(N-端),Xpress Epitope Tag(N-端), EK 切割位點 |
| 載體抗性: | 氨芐青霉素(Ampicillin) |
| 克隆菌株: | TOP10 |
| 表達菌株: | 推薦LMG194 |
| 備注: |
pBAD/His A載體是阿拉伯糖調控載體; 在無葡萄糖的培養基中,阿拉伯糖正向調控目的基因 的表達; 通過調節阿拉伯糖的濃度水平來優化目的蛋白的可溶性表達; pBAD/His A,B,C之間僅閱讀框不同。 |
| 產品目錄號: | V430-01 |
| 穩定性: | 穩表達 |
| 組成型/誘導型: | 誘導型(阿拉伯糖) |
| 病毒/非病毒: | 非病毒 |
pBad/His A載體質粒圖譜和多克隆位點信息
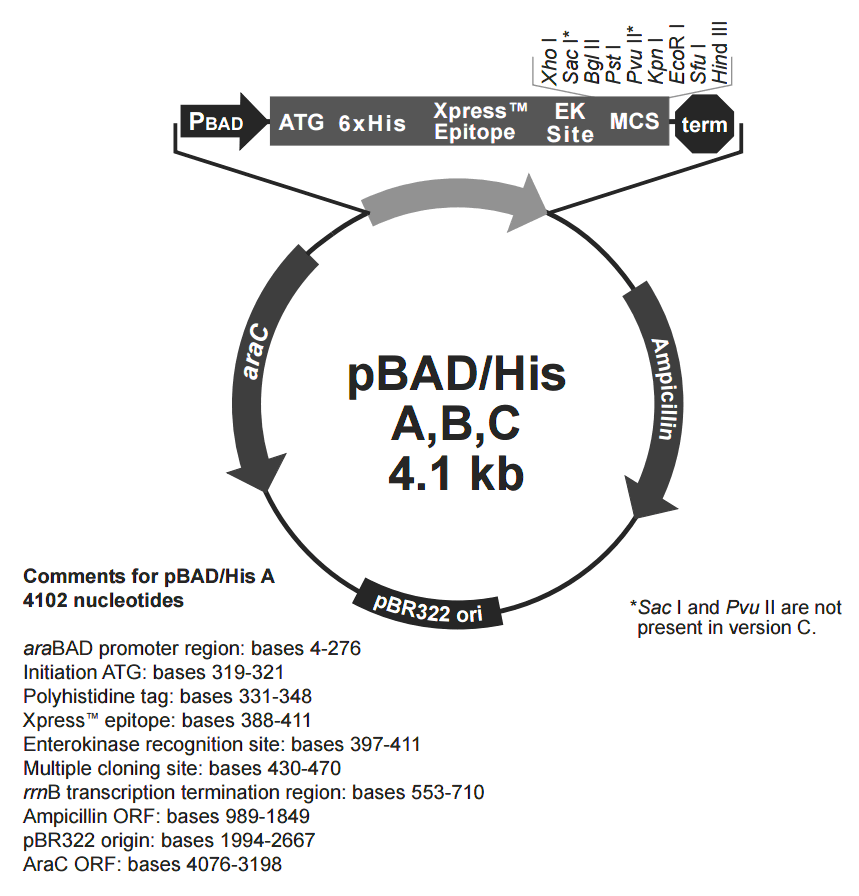
pBad/His A載體簡介
pBAD/His和PBAD/Myc-His載體質粒是衍生于pBR322載體。載體設計用來在大腸桿菌中進行可調節,劑量依賴性的表達和純化重組目的蛋白。使用大腸桿菌araBAD啟動子(pBAD)增強了大腸桿菌重組蛋白可溶性表達的水平。pBAD/His和pBAD/Myc His載體上的調節蛋白AraC能夠調控pBad啟動子。
pBAD/His A,B,C 載體介紹 The pBAD/His Kit provides all of the necessary reagents to express your protein in a tightly regulated fashion.
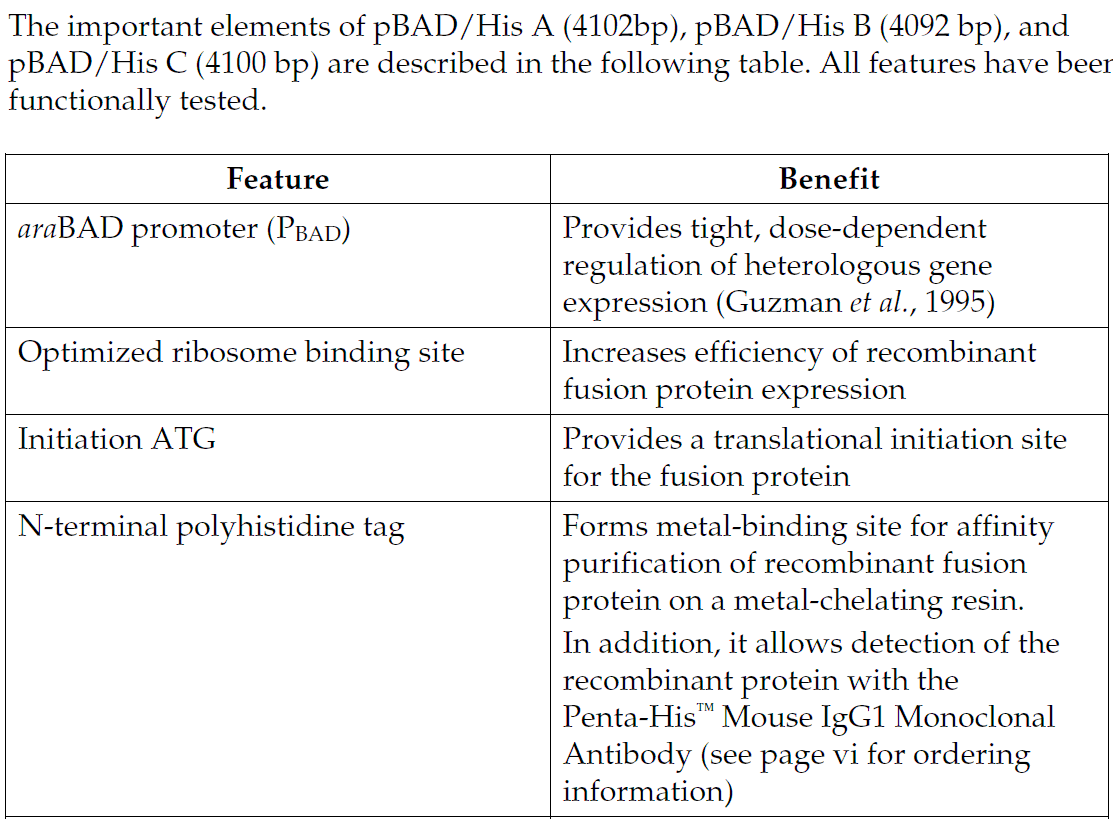
The vector pBAD/His allows you to express your protein with an N-terminal tag. The vector provides:
The araBAD promoter for tightly regulated expression
Translation initiation signals optimized for E. coliexpression
N-terminal polyhistidine (6xHis) tag for purification with nickel-chelating resin and detection with an Anti-
HisG Antibody
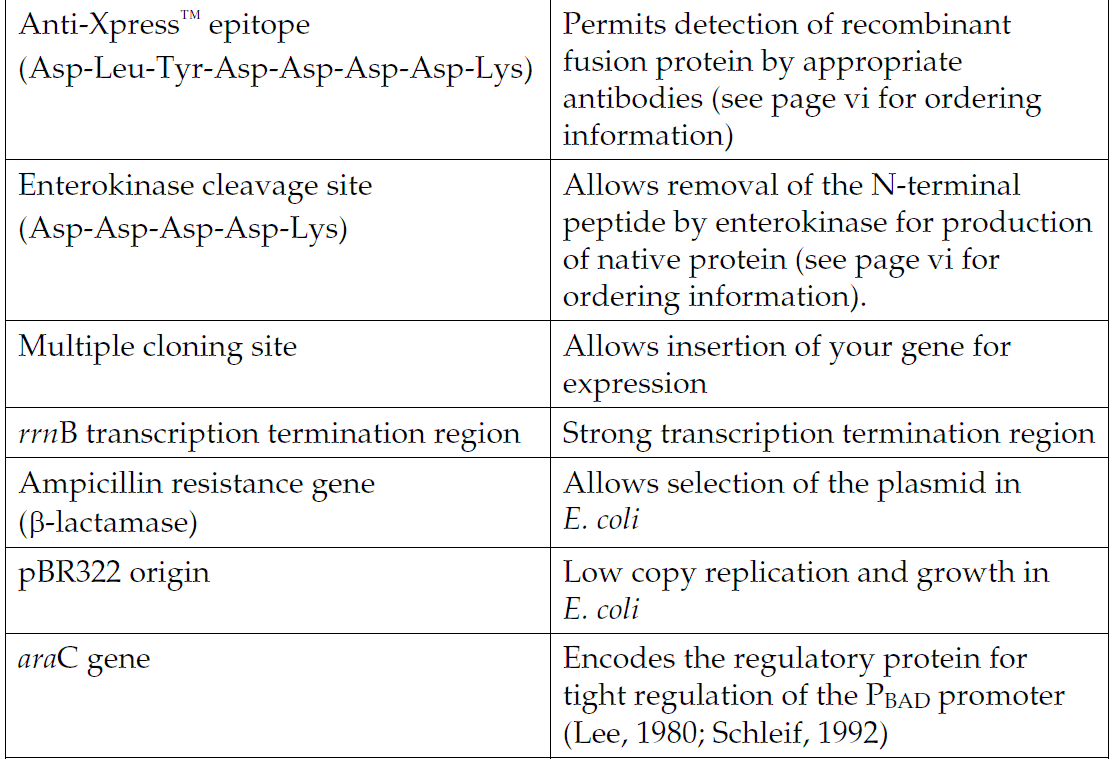
N-terminal Xpress epitope for detection and analysis with an Anti-Xpress Antibody
Enterokinase cleavage site for removing the N-terminal tag following purification
Three vectors are provided (A, B, and C). Each has the N-terminal tag in a different reading frame relative to the multiple cloning site to simplify in-frame cloning of your gene.
The pBAD/His and pBAD/Myc-His plasmids are pBR322-derived expression vectors designed for regulated, dose-dependent recombinant protein expression and purification in E. coli. Optimum levels of soluble, recombinant protein are possible using the araBAD promoter (PBAD) from E. coli. The regulatory protein, AraC, is provided on the pBAD/His and pBAD/Myc-His vectors allowing regulation of PBAD. L-阿拉伯糖調控表達 In the presence of L-arabinose, expression from PBAD is turned on while the absence of L-arabinose produces very low levels of transcription from PBAD (Lee, 1980; Lee et al., 1987). Uninduced levels are repressed even further by growth in the presence of glucose. Glucose reduces the levels of 3′,5′-cyclic AMP, thus lowering expression of the catabolite-repressed PBAD promoter (Miyada et al., 1984). By varying the concentration of L-arabinose, protein expression levels can be optimized to ensure maximum expression of soluble protein. In addition, the tight regulation of PBAD by AraC is useful for expression of potentially toxic or essential genes (Carson et al., 1991; Dalbey and Wickner, 1985; Guzman et al., 1992; Kuhn and Wickner, 1985; Russell et al., 1989; San Millan et al., 1989). For more information on the mechanism of expression and repression of the ara regulon, refer to Schleif, 1992.
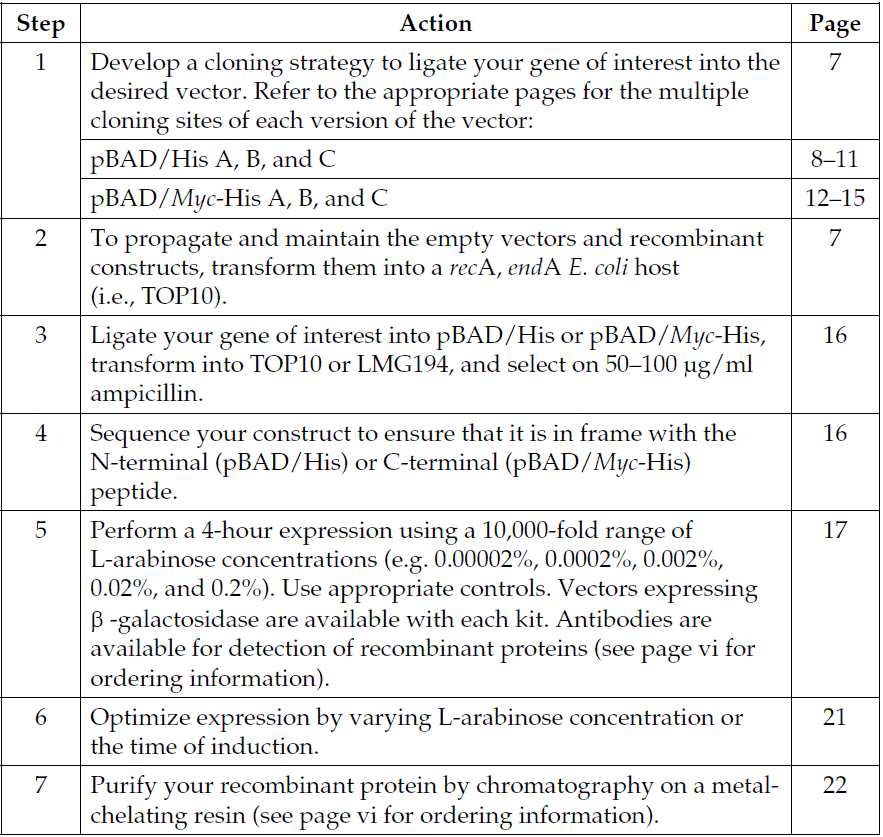
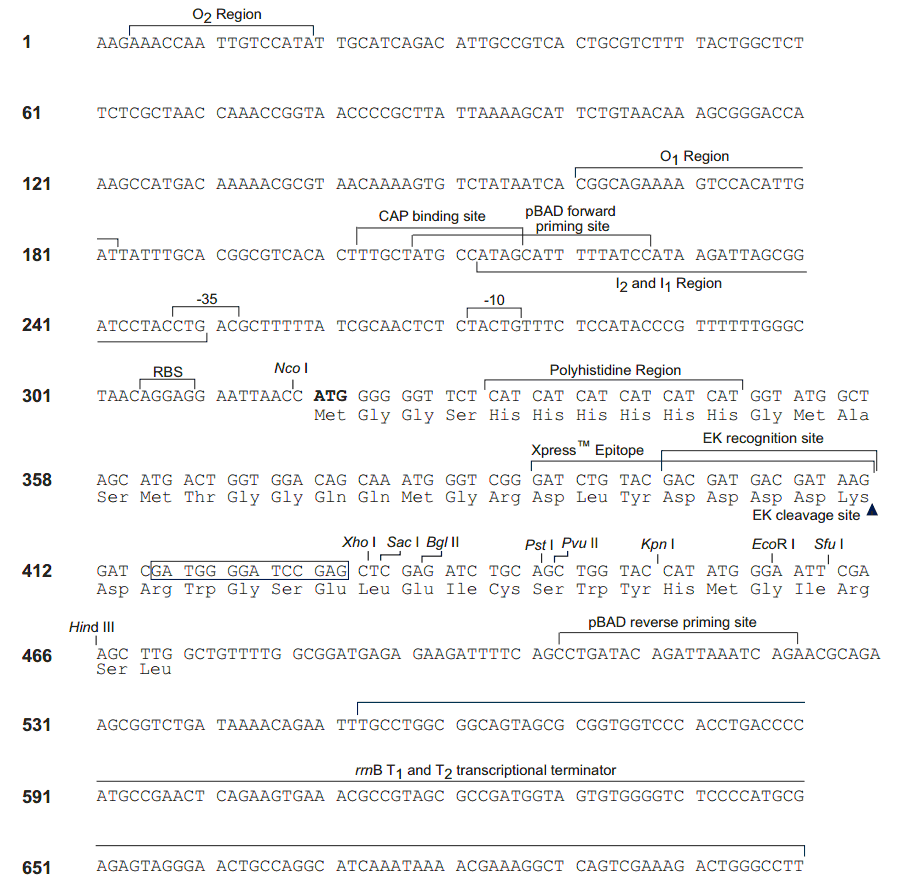
pBad/His A載體序列
hz-0549R Collagen III 抗Ⅲ型膠原抗體 Collagen Ⅲ
hz-0948R Collagen III 抗Ⅲ型膠原抗體
hz-5764R CIAPIN1 細胞因子誘導凋亡抑制因子1
hz-0806R Collagen IV/Arresten 抗IV型膠原抗體
hz-0552R Collagen V Ⅴ型膠原抗體
hz-4595R Collagen IV 抗IV型膠原抗體
hz-0553R Collagen VI alpha 1 抗Ⅵ型膠原抗體
hz-5765R LANCL2 G蛋白偶聯受體69B
hz-1558R Collagen VII 7型膠原抗體
hz-5766R RAB6C RAS癌基因相關蛋白Rab6C抗體
hz-5767R Epigen 上皮細胞有絲分裂蛋白抗體
hz-2921R PAR3 非典型蛋白激酶C特定相互作用蛋白抗體
hz-0554R Collagen X Ⅹ型膠原抗體
hz-5044R COL4A3BP IV型膠原α3結合蛋白抗體
hz-2924R Collagen XI alpha 2 膠原蛋白11A2抗體
hz-1428R Claudin 1 緊密連接蛋白1抗體
hz-2788R Claudin 3 緊密連接蛋白3抗體
hz-2790R Claudin 4 緊密連接蛋白4抗體
hz-2760R Cortactin 皮層肌動蛋白抗體
hz-3100R phospho-Cortactin (Tyr466) 磷酸化皮層肌動蛋白抗體
hz-1553R Claudin 5 緊密連接蛋白5抗體
關于我們
產品中心
服務中心
Copyright@ 2003-2025
上海滬震實業有限公司版權所有
電話:021-60345367
傳真:021-31320307
地址:上海市楊浦區密云路1018號復旦科技園808室
郵編:200612

